 |
OpenPFC
0.1.4
Phase Field Crystal simulation framework
|
 |
OpenPFC
0.1.4
Phase Field Crystal simulation framework
|
Describes a static, pure partitioning of the global simulation domain into local subdomains. More...
#include <decomposition.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| Decomposition (const World &world, const Int3 grid) | |
Public Attributes | |
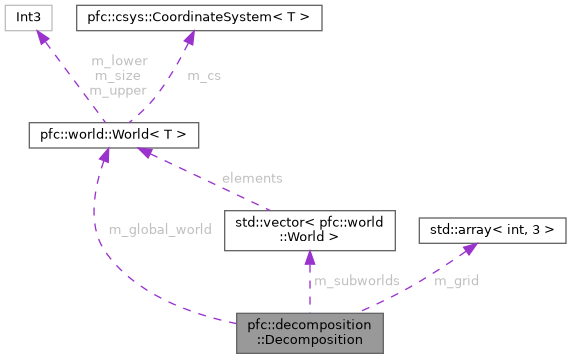
| const pfc::World & | m_global_world |
| The World object. | |
| const std::array< int, 3 > | m_grid |
| The number of parts in each dimension. | |
| const std::vector< pfc::World > | m_subworlds |
| The sub-worlds for each part. | |
Friends | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const Decomposition &d) |
Describes a static, pure partitioning of the global simulation domain into local subdomains.
The Decomposition struct encapsulates how the global World domain is split across compute units, such as MPI processes, OpenMP threads, or GPU tiles. It represents the ownership layout, not how communication is performed.
Each Decomposition instance defines the local subdomain assigned to the current compute entity, including bounding box, size, and global offset. It provides a consistent, backend-independent view of how the World is subdivided.
pfc::decomposition namespace.DecompositionRequest, and decomposition is created to satisfy that request.Decomposition supports an inversion of control model where DifferentialOperator (or any backend) declares its layout requirements via a DecompositionRequest:
This request is passed to the decomposition builder:
This design allows:
The decomposition system is extensible by:
SplitStrategy) or request properties.